esprit (n.)
1590s, "liveliness, wit, vivacity," from French esprit "spirit, mind," from Old French espirit "spirit, soul" (12c.), from Latin spiritus "spirit" (see spirit (n.)). For initial e-, see e-.
Esprit de corps, recorded from 1780 in English, preserves the usual French sense. French also has the excellent phrase esprit de l'escalier, literally "spirit of the staircase," defined in OED as, "a retort or remark that occurs to a person after the opportunity to make it has passed." It also has esprit fort, a "strong-minded" person, one independent of current prejudices, especially a freethinker in religion.
Entries linking to esprit
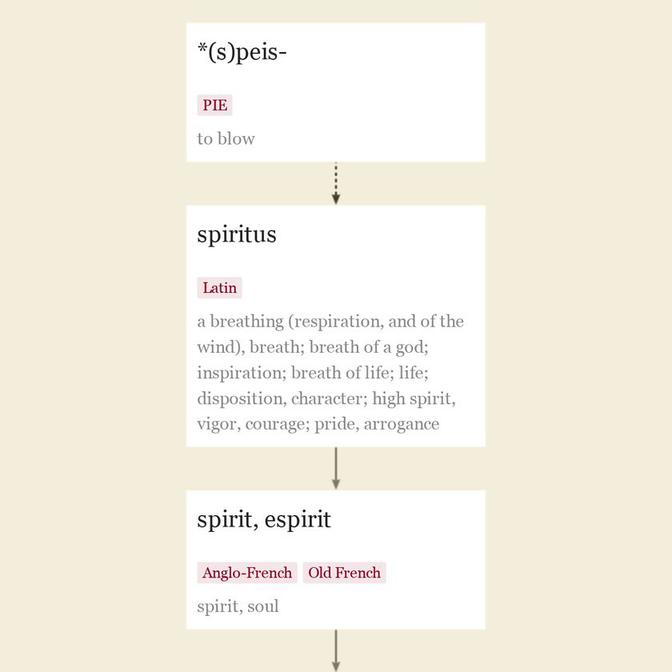
mid-13c., "life, the animating or vital principle in man and animals," from Anglo-French spirit, Old French espirit "spirit, soul" (12c., Modern French esprit) and directly from Latin spiritus "a breathing (of respiration, also of the wind), breath;" also "breath of a god," hence "inspiration; breath of life," hence life itself.
The Latin word also could mean "disposition, character; high spirit, vigor, courage; pride, arrogance." It is a derivative of spirare "to breathe," and formerly was said to be perhaps from a PIE *(s)peis- "to blow" (source also of Old Church Slavonic pisto "to play on the flute"). But de Vaan says the Latin verb is "Possibly an onomatopoeic formation imitating the sound of breathing. There are no direct cognates." Compare conspire, expire, inspire.
In English it is attested from late 14c. as "divine substance, divine mind, God;" also "Christ" or His divine nature; also "the Holy Ghost; divine power." Also by late 14c. as "the soul as the seat of morality in man," and "extension of divine power to man; inspiration, a charismatic state; charismatic power," especially in reference to prophecy.
The meaning "supernatural immaterial creature; angel, demon; an apparition, invisible corporeal being of an airy nature" is attested from mid-14c. The word is attested by late 14c. as "ghost, disembodied soul of a person" (compare ghost (n.)). Spirit-rapping, colloquial for spiritualism in the supernatural sense, is from 1852. Spirit-world "world of disembodied spirits" is by 1829.
It is attested from late 14c. as "essential nature, essential quality." The non-theological sense of "essential principle of something" (as in Spirit of St. Louis) is attested from 1680s and was common after 1800. The Spirit of '76 in reference to the qualities that sparked and sustained the American Revolution of 1776 is attested by 1797 in William Cobbett's "Porcupine's Gazette and Daily Advertiser."
It also is attested from mid-14c. in English as "character, disposition; way of thinking and feeling, state of mind; source of a human desire;" in Middle English freedom of spirit meant "freedom of choice." It is attested from 1580s in the metaphoric sense of "animation, vitality," and by c. 1600 as "frame of mind with which something is done," also "mettle, vigor of mind, courage."
From late 14c. in alchemy as "volatile substance; distillate" (and from c. 1500 as "substance capable of uniting the fixed and the volatile elements of the philosopher's stone"). Hence spirits "volatile substance;" the sense of which narrowed to "strong alcoholic liquor" by 1670s. This also is the sense in spirit level (1768), so called for the liquid in the clear tube.
According to Barnhart and OED (1989), the earliest use of the word in English mainly is from passages in the Vulgate, where the Latin word translates Greek pneuma and Hebrew ruah. A distinction between soul and spirit (as "seat of emotions") became current in Christian terminology (such as Greek psykhē and pneuma, Latin anima and spiritus) but "is without significance for earlier periods" [Buck]. Latin spiritus, usually in classical Latin "breath," replaced animus in the sense "spirit" in the imperial period and appears in Christian writings as the usual equivalent of Greek pneuma.
in brief, conceive light invisible, and that is a spirit. [T. Browne, " Religio Medici"]
"a lively frolic, rowdy drinking bout," 1804, slang or colloquial, earliest in Scottish dialect works, a word of uncertain origin. Perhaps [Barnhart] an alteration of French esprit "lively wit" (see esprit). According to Klein, Irish spre seems to be a loan-word from Old Norse sprakr. Watkins proposes a possible origin as an alteration of Scots spreath "cattle raid," from Gaelic sprédh, spré, "cattle; wealth," from Middle Irish preit, preid, "booty," ultimately from Latin praeda "plunder, booty" (see prey (n.)).
Anatoly Liberman (blog post Dec. 13, 2023) does not object to a Celtic origin, but points to the similar "skeleton" in spree, spark, sprinkle, Latin spargo (see sparse), and suggests "the sound group spr seems to have suggested to speakers the idea of spontaneous, unregulated growth."
The splore is a frolic, a merry meeting. In the slang language of the inhabitants of St Giles's, in London, it is called a spree or a go. [Note in "Select Scottish Songs, Ancient and Modern," vol. II, London, 1810]
In Foote's comedy "The Maid of Bath" (1794) the word appears as a Scottish dialect pronunciation of spry: " 'When I intermarried with Sir Launcelot Coldstream, I was en siek a spree lass as yoursel; and the baronet bordering upon his grand climacteric;' " etc.
the later Romans evidently found words beginning in sc-, sp-, st- difficult or unpleasant to pronounce; in Late Latin forms begin to emerge in i- (such as ispatium, ispiritu), and from 5c. this shifted to e-. The development was carried into the Romanic languages, especially Old French, and the French words were modified further after 15c. by natural loss of -s- (the suppression being marked by an acute accent on the e-), while in other cases the word was formally corrected back to the Latin spelling (for example spécial). Hence French état for Old French estat for Latin status, etc. It also affected Romanic borrowings from Germanic (such as espy, eschew).
A different e- is a reduced form of Latin ex- before consonants (see ex-), and the e- in enough is an unfelt survival of an Old English alternative form of ge-.
Trends of esprit
More to Explore
updated on September 27, 2021